9th Physics Motion
Class 9th Science -Physics
ICSE/ CBSE Notes-By Er. Amit Singh
For more Notes click this link https://cbsenotesallsub.blogspot.com/
MOTION
a-State of rest
b-State of motion
The motion is the change in position of an object with respect to its surroundings in a given interval of time.
motion can be described by terms -
- 1-distance
- 2-displacement
- 3-speed
- 4-velocity
- 5-time
- 6-acceleration
Uniform motion and non-uniform motion
Uniform motion
- When an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time it is in uniform motion.
- The distance time graph for uniform motion is a straight line.
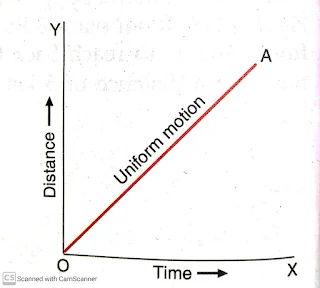 |
| Uniform motion |
Non-uniform motion
- When an object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time it is said to be in non-uniform motion.
- The distance -time graph for a body having non uniform motion is a curved line
.jpeg) |
| Non Uniform motion |
Vectors and Scalar Quantities:
eg- distance , time ,mass, energy etc
·
Vectors v/s Scalar Quantities
Vectors Quantities | Scalar Quantities |
It can be specified by both magnitude and direction | It can be specified by only magnitude |
These physical quantities follow the rule of vector algebra | These physical quantities not follow the rule of vector algebra |
Eg velocity ,force weight , momentum etc | Eg temperature ,mass, energy ,density etc |
Distance and Displacement
Distance-
- It is defined as the length of the actual path traveled by the body .
- It is a scalar quantity
- It can never be negative
- It is always greater or equal to the displacement in any direction
Displacement-
- It is defined as the shortest distance between the initial and final position of a moving object
- Displacement always a straight line joining both points
- It is a vector quantity
- It can be positive , negative and zero
- It is always less than or equal to the distance
SPEED
- Speed of the body is distance travelled by it per unit time.
- speed of a body gives us an idea of how slow or fast that body is moving.
- SI unity of speed is m/s .
- Speed also express in Kmph means kilometres per hours .
- speed is scalar quantity.
- speed of running car is measured by Speedometer.
- Distance travelled by any object is measured by Odometer.
- The average speed of the body is the total distance travelled divided by total time taken.
- Average speed = Total distance Travelled / Total time taken.
Velocity
- Velocity of a body is distance travelled by it per unit time in a given direction.
- Velocity = Displacement / Time taken (V= d/t)
- SI Unit of velocity is m/s .
- Velocity is a vector quantity.
- A body is said to be moving with uniform velocity if it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time in a specified direction.
- For Example a scooter moving with a constant speed along a straight line.
- A body is said to be moving non uniform velocity if it covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time
- For Example a cycle moving on a straight road with variable speed
- Average velocity is the ratio of total displacement of a body to time taken.
- it is also written as - Average velocity = Total Displacement / Total time taken
- Average velocity = (initial velocity + Final velocity)/ 2
Acceleration (Rate of change of velocity)
- Acceleration of a body is defined as the rate of change of its velocity with time.
- The SI unit of acceleration is m/s square .
- Acceleration = Change in velocity / time taken for change
- change in velocity = Final velocity - initial velocity
- acceleration a = (v-u)/t
- Acceleration is a vector quantity and can be positive ,negative and zero.
- If the velocity of an object increases , then the object said to be moving with positive acceleration. In this case ( v > u) , a is positive
- If the velocity of an object decreases , then the object said to be moving with negative acceleration . In this case (v < u ), a is negative
- If the change in velocity is Zero , ie Either the object remains at rest or moving with uniform velocity . In this case (v =u ) , a is zero
- It is also called Deceleration or Negative Acceleration.
- it is acceleration with the negative sign.
- if final velocity less than initial velocity then acceleration is negative.
- its unit is same as the acceleration.
Equations of Uniformly Accelerated Motion
- First Equation of motion
- Second Equation of motion
- Third Equation of motion


.jpeg)
.jpeg)



Comments
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box..