class 10th Light ,Reflection and Refraction
CLASS 10th
ICSE/ CBSE Notes-By Er. Amit Singh
For more Notes click this link https://cbsenotesallsub.blogspot.com/
Light-Reflection and Refraction
what is light ?
- Light is the form of energy that enable us to see.
- There are a number of common wonderful phenomena associated with light such as -
- image formation by mirrors
- The twinkling of stars.
- The beautiful colours of rainbow
- Bending of light
Properties of light
- It is electromagnetic wave so does not require any medium to travel.
- Light tends to travel in straight line.
- Light has dual nature i.e. wave as well as particle.
- Light casts shadow.
- Speed of light is maximum in vaccum.
- when light falls on a surface following may happen.
- Reflection
- Refraction
- Absorption
Reflection
Reflection : Bouncing of light when it strikes on a polished surface like mirror.
- A highly polished surface such as a mirror reflects most of the light falling on it.
according to law of reflection:
- Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- The incident ray and the Normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
what is Image ?
- It is a point where atleast two light rays actually meet or appear to meet.
- we can also say that for making any image required minimum two rays.
- There are two types of image
- Real Image:
- it formed when light rays actually meet.
- it can be obtained on screen.
- it is inverted
- Eg image formed on cinema screen
2. Virtual image:
- it formed when light ray appear to meet.
- it can not obtained on screen.
- it is erect.
- Eg image formed by convex mirror
what is Mirror ?
- A mirror is a Reflective surface that bounces off light , which producing either a real image or a virtual image.
- when any object is placed in front of mirror the image of the same object is seen in the mirror.
- The object is the source of incident ray and image formed by incident rays.
Types of Mirror
There are two types of mirror:
- Plane Mirror
- A plane mirror is a flat mirror which have smooth reflective surface.
- Plane mirror always forms a virtual image ,have same shape and size as the object.
- it make virtual and erect image.
- Size of image is equal to the size of the object.
- Image is formed as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
- plane mirror formed laterally inverted image.
- it means the right side of the object appears left side of the image and vice -versa.
- eg Due to this reason the word AMBULANCE is written as reverse order with reverse letters.

2 .Spherical Mirrors
- Mirrors those reflecting surface is curved are called spherical mirrors.
- The reflecting surface of a spherical mirror may be curved inwards or outwards.
- There are two types of spherical mirrors concave mirror and convex mirror.
Concave Mirror
- A spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards ,which is faces towards the center of the sphere is called a concave mirror.
- it is called conversing mirror.
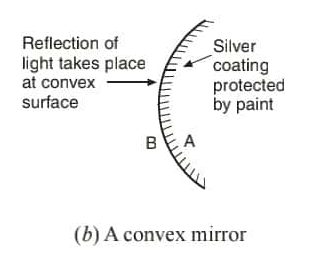
Convex Mirror
- A spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved outward is called a convex mirror.
- it is called diverging mirror

- The front side of the shinning steel spoon is a concave mirror where as its back side is a convex mirror.
Some important terms

- Principal axis- The line joining the pole and center of curvature.
- Pole(P)- The center of the spherical mirror.
- Aperture- It is the effective diameter of the spherical mirror.
- Center of curvature(C) It is the center of hollow glass sphere
- Radius of curvature (R) The distance between the pole and the center of curvature.
- Focus(F) The point on principal axis where all the parallel light ray actually meet or appear to meet after reflection.
- Focal length(f) The distance between pole and focus .
- R= 2f
Rules for making Ray diagrams by concave mirror
Rule -1 A ray parallel to the principal axis will passes through the principal focus after reflection.

Rule-2 A ray passing through the principal focus of concave mirror will emerge parallel to principal axis after reflection.
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)




Thank you sir
ReplyDeleteNice Blog! Thanks for sharing amazing information with us,for more visit best cbse boarding schools in bihar
ReplyDeleteThankyou so much sir 🙏🙂🙂🙂🙏🏻
ReplyDeleteThanks 👍 dir
ReplyDeleteVery knowledgeable content thank you sir
ReplyDeleteuseful notes
ReplyDeleteThank you so much sir 🙏🏻
ReplyDeleteThank you so much sir 🙏🏻
ReplyDelete